MKSAP quiz: Woman complains of joint pain and stiffness
A 56-year-old woman is evaluated for a 2-year history of joint pain and stiffness of the hands. The appearance of her hands on physical examination is shown.
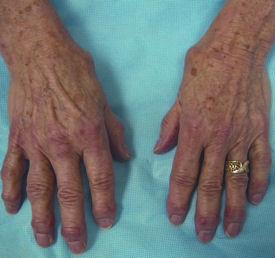
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
A. Acetaminophen
B. Methotrexate
C. Prednisolone
D. Etanercept
Answer and critique
The correct answer is A. Acetaminophen
This item is available online to MKSAP subscribers in the Rheumatology section, Item 40.
Acetaminophen is an effective, inexpensive treatment for osteoarthritis. This agent also is safe, particularly compared with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. This patient has squaring of the first carpometacarpal joints and bone hypertrophy in several distal interphalangeal joints, which are characteristic findings in osteoarthritis.
Double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have shown that acetaminophen effectively manages symptoms of osteoarthritis in many patients. However, the relative efficacy of acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs remains controversial among many experts. Some experts believe that acetaminophen should be the drug of choice for osteoarthritis, whereas others argue that recent data prove the superiority of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for patient preference in relieving symptoms.
A study testing a program in which physicians were educated to discontinue use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis in elderly patients showed that these agents could be replaced with acetaminophen without worsening of pain. These results suggest that patients with osteoarthritis who have high risk for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug complications may use alternate therapy with acetaminophen without compromising pain control.
Methotrexate is appropriate for management of rheumatoid arthritis. However, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus are not associated with involvement of the distal interphalangeal joints and deforming arthritis, respectively, which are both clearly present in this patient.
Corticosteroids, such as prednisolone, are potent anti-inflammatory agents. However, use of these agents would not benefit this patient, because osteoarthritis is not a systemic inflammatory disease. In addition, long-term use of corticosteroids is associated with significant adverse side effects. Etanercept is an appropriate therapy for the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis but is not indicated for osteoarthritis.
Key Points
- Acetaminophen is an effective, safe and inexpensive treatment for osteoarthritis.
- Patients with osteoarthritis who have high risk for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug complications may use alternate therapy with acetaminophen, often without compromising pain control.



