MKSAP Quiz: 2-month history of painless, violaceous skin nodules with edema
A 32-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-month history of painless, violaceous skin nodules with surrounding edema on the chest, back, and lower extremities. He reports that he has sex with men. Medical history is significant for AIDS, with a CD4 cell count of 54/µL. He is not following an antiretroviral therapy regimen.
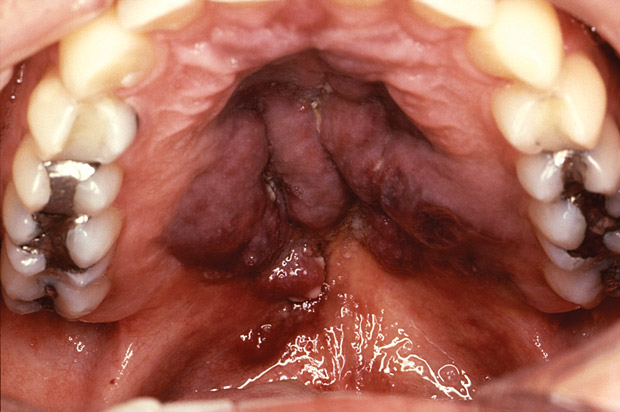
On physical examination, temperature is 38.1°C (100.5°F), blood pressure is 135/62 mm Hg, pulse rate is 68/min, and respiration rate is 20/min. Several nodules are seen in the mouth during oral examination (shown).
Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
A: Cytomegalovirus
B: Epstein-Barr virus
C: Human herpes virus type 6
D: Human herpes virus type 8
Answer and critique
The correct answer is D. Human herpes virus type 8. This item is Question 47 in MKSAP 18's Infectious Disease section.
This patient has Kaposi sarcoma caused by human herpes virus (HHV) type 8. It is found primarily in men who have sex with other men and who have AIDS. This patient's clinical presentation is typical for Kaposi sarcoma, with painless violaceous skin nodules with oral involvement. The treatment for Kaposi sarcoma includes antiretroviral therapy, local therapies (radiation therapy, intralesional chemotherapy, cryotherapy, or topical retinoids), and systemic therapies such as interferon or chemotherapy.
Cytomegalovirus (HHV-5) infections are most commonly asymptomatic, but they can also present with a mononucleosis-like syndrome and may reactivate in patients with cellular immunodeficiency such as AIDS or in those who have had a solid organ or bone marrow transplantation. Cytomegalovirus does not cause skin nodules but can present with retinitis (in AIDS), pneumonia, hepatitis, adrenalitis, pancytopenia, gastritis, or colitis.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (HHV-4) is the main cause of infectious mononucleosis presenting with fever, exudative pharyngitis, cervical lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly. EBV reactivation is associated with the development of T-cell and B-cell lymphomas, Hodgkin and Burkitt lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in solid organ transplantation.
Human herpes virus type 6 causes roseola infantum, febrile seizures in children, and cytomegalovirus-seronegative and EBV-seronegative mononucleosis. It does not cause skin nodules. Recipients of bone marrow transplantation may also develop encephalitis, hepatitis, pneumonia, rash, graft-versus-host disease, and delayed engraftment.
Key point
- Kaposi sarcoma can develop in patients with AIDS infected with human herpes virus type 8, presenting with painless violaceous skin nodules with oral involvement.